In the world of modern manufacturing, CNC machines have revolutionized the production of precision parts. Two popular types of CNC machines are machining centers and turning centers. While they may appear similar on the surface, there are distinct differences between them that make each of them suitable for specific manufacturing requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- Machining centers are versatile and precise CNC machines that offer diverse machining processes, high accuracy, and automation.
- Turning centers, also known as lathes, excel at rotational machining operations, provide excellent surface finish, and are suitable for high-volume production.
- When choosing between a machining center and a turning center, consider factors such as the project’s geometries and complexity, the need for cylindrical parts and high volume, automation and precision requirements, and versatility.
- The primary differences between machining centers and turning centers lie in their functions, supported processes, tool features, uses, cutting attributes, and the type of chips produced.
- CNC turning involves rotational machining using a lathe machine to shape cylindrical parts, while CNC milling utilizes cutting tools and multiple axes to machine complex parts.
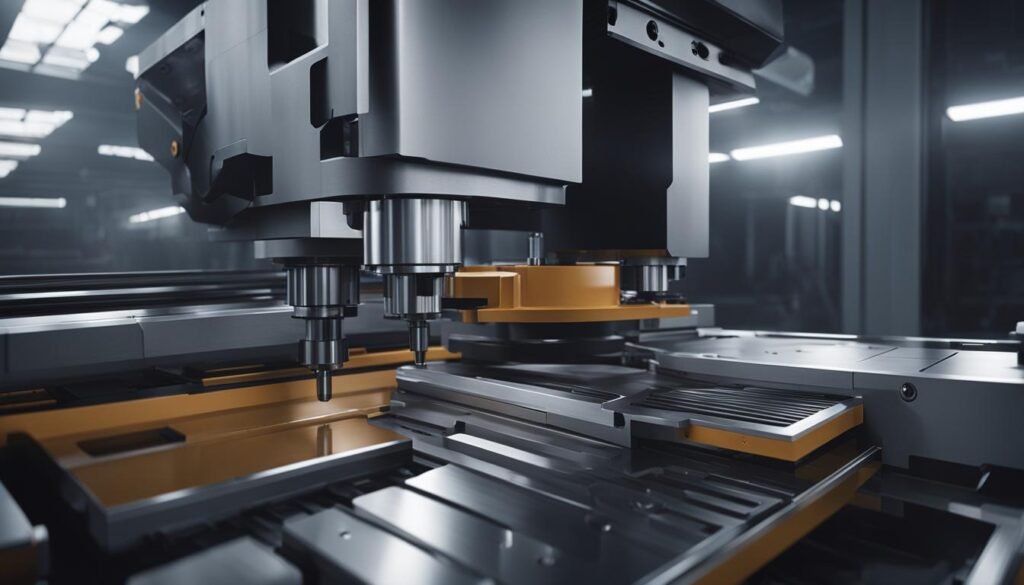
Machining Centers: Versatile and Precise
In the world of CNC machining, machining centers are highly versatile and precise machines. They encompass a wide range of machining processes, including milling, drilling, tapping, and more. This versatility allows manufacturers to perform various operations on a single machine, reducing the need for multiple setups and tool changes.
One of the key advantages of machining centers is their ability to perform multi-axis machining. With multiple axes of movement, these machines can create complex geometries and shapes with high accuracy. This is particularly important for industries that require intricate parts and components, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
Automation is another significant feature of machining centers. These machines can be equipped with automatic tool changers, pallet changers, and robotic systems, allowing for continuous production with minimal manual intervention. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces the risk of errors and increases overall productivity.
The versatility and precision of machining centers make them invaluable in various industries. Whether it’s producing small intricate parts or large components, these machines offer diverse machining processes, high accuracy, and automation, making them an essential tool in modern manufacturing.

Machining Centers: Versatile and Precise
Turning Centers: Specialized in Rotational Machining
In the world of CNC machining, turning centers, also known as lathes, play a crucial role in rotational machining operations. These specialized machines excel at shaping cylindrical parts and components with high precision and excellent surface finish. Whether you’re producing one-off prototypes or high-volume production runs, turning centers offer the versatility and efficiency required for your manufacturing needs.
One of the key advantages of turning centers is their ability to perform single-axis machining. The workpiece rotates while the cutting tool remains stationary, allowing for precise shaping and cutting operations. This makes turning centers ideal for creating round or cylindrical parts, such as shafts, pins, and valves. The ease of setup and programming further enhances their efficiency, making them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale production.
Turning centers are particularly well-suited for high-volume production due to their continuous rotational machining capabilities. The consistent and controlled movement of the workpiece ensures uniformity in shape and size, which is essential for mass production. Additionally, turning centers offer excellent surface finish, resulting in high-quality parts that meet the most demanding specifications.
Turning Centers vs. Machining Centers
While machining centers excel at versatile milling, drilling, and tapping processes, turning centers provide specialized functionality for rotational machining. While both machines are essential in modern manufacturing, their distinct capabilities and applications make them suitable for different production requirements. The table below highlights the key differences between turning centers and machining centers:
| Turning Centers (Lathes) | Machining Centers |
|---|---|
| Specialized in rotational machining operations | Versatile for milling, drilling, and tapping |
| Single-axis machining | Multi-axis machining |
| Excellent surface finish | Diverse machining processes |
| Ideal for high-volume production | Automation capabilities |
| Easy setup and programming | Wide range of workpiece shapes |
Machining Center and Turning Center Comparison
When it comes to CNC machining, understanding the difference between a machining center and a turning center is essential. These two types of machines have distinct features and applications that make them suitable for different manufacturing requirements. In this section, we will compare machining centers and turning centers in terms of machining processes, axes movement, workpiece shapes, applications, precision, surface finish, automation, setup and programming, and their suitability for production.
Machining Processes and Axes Movement
One of the key differences between machining centers and turning centers lies in the machining processes they can perform and their axes movement capabilities. Machining centers, with their multi-axis movement, are versatile machines capable of milling, drilling, tapping, and various other processes. They can handle complex geometries and are ideal for machining parts with intricate features.
On the other hand, turning centers, also known as lathes, specialize in rotational machining operations. They excel at creating cylindrical parts and components and provide single-axis machining. While they may not offer the same level of flexibility as machining centers, turning centers are highly efficient when it comes to producing cylindrical parts in high volume.
Workpiece Shapes and Applications
Another significant difference between machining centers and turning centers is the type of workpiece shapes they can handle. Machining centers are suitable for machining parts with complex geometries, including 3D contours and sculpted surfaces. They are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and mold making, where precision and intricate designs are paramount.
Turning centers, on the other hand, are designed for rotational machining, making them ideal for producing cylindrical parts, shafts, and other rotational components. They find applications in industries such as automotive, oil and gas, and general manufacturing, where high-volume production of cylindrical parts is required.
Precision, Surface Finish, and Automation
When it comes to precision and surface finish, both machining centers and turning centers can achieve high levels of accuracy. Machining centers, with their multi-axis movement and advanced tooling options, offer excellent precision and surface finish for intricate parts. They are also well-suited for automation, with the ability to integrate robotics and other automated systems into the machining process.
Turning centers, on the other hand, provide exceptional surface finish for cylindrical parts due to their rotational machining capabilities. They are also known for their ease of setup and programming, making them efficient for high-volume production. However, they may have limitations in terms of complex geometries and the level of automation that can be achieved compared to machining centers.
In summary, machining centers and turning centers have distinct features and applications that make them suitable for different manufacturing requirements. While machining centers offer versatility and precision for complex parts, turning centers excel at producing cylindrical parts in high volume. Understanding their differences can help manufacturers make informed decisions when choosing the right machine for their production needs.

Choosing the Right Machine for Your Needs
When it comes to selecting the right machine for your manufacturing project, understanding the differences between a machining center and a turning center is crucial. Various factors play a role in determining the most suitable option, including the geometries and complexity of the parts, the need for cylindrical components and high-volume production, automation and precision requirements, and the desired level of versatility.
Geometries and Complexity: If your project involves intricate geometries or complex parts, a machining center might be more appropriate. With its multi-axis movement capability, the machining center allows for precise and intricate machining processes like milling, drilling, and tapping.
Cylindrical Parts and High Volume: Turning centers excel at rotational machining operations, making them ideal for projects that require cylindrical parts. If you have a high-volume production requirement for cylindrical components, a turning center’s single-axis machining capability can provide efficient and reliable results.
Automation and Precision: If automation and precision are top priorities, a machining center with its advanced automation features may be the preferred choice. Machining centers offer high accuracy and the ability to automate various machining processes, increasing productivity and ensuring consistent results.
Versatility: When it comes to versatility, both machining centers and turning centers have their advantages. Machining centers are known for their ability to perform a wide range of machining processes, offering flexibility in manufacturing operations. On the other hand, turning centers, with their specialized focus on rotational machining, provide excellent surface finish and are suitable for high-volume production.
| Machining Center | Turning Center | |
|---|---|---|
| Geometries and Complexity | Multi-axis movement enables precise machining of intricate geometries and complex parts. | Specialized for rotational machining, ideal for cylindrical components. |
| Cylindrical Parts and High Volume | Limited capability for cylindrical parts, but can handle high-volume production. | Single-axis machining specializes in cylindrical parts, suitable for high-volume production. |
| Automation and Precision | Advanced automation features, high precision. | Less automation, but excellent precision and surface finish. |
| Versatility | Offers a wide range of machining processes and flexibility. | Specialized in rotational machining and provides excellent surface finish. |
Top 6 Differences Between Machining Centers and Turning Centers
When it comes to CNC machining, understanding the differences between machining centers and turning centers is essential. These two types of machines have distinct features and capabilities that make them suitable for different applications. Let’s take a closer look at the top six differences between machining centers and turning centers.
1. Primary Function
A machining center is primarily used for milling, drilling, tapping, and other machining processes that involve the removal of material from a workpiece. On the other hand, a turning center, also known as a lathe, is specialized in rotational machining, where the workpiece rotates against the cutting tool.
2. Processes Supported
Machining centers support a wide range of processes, including multi-axis machining, making them highly versatile. In contrast, turning centers are focused on single-axis rotational machining operations.
3. Tool Features
Machining centers typically have a variety of tool holders that allow for the use of different cutting tools, such as end mills, drills, and taps. Turning centers, on the other hand, use tool holders specifically designed for turning operations, such as turning inserts and boring bars.
4. Uses
Machining centers are ideal for machining complex parts with intricate geometries, while turning centers excel at creating cylindrical parts. This makes turning centers a popular choice for high-volume production of components such as shafts and bushings.
5. Cutting Attributes
When it comes to cutting, machining centers typically produce more chips due to their milling and drilling operations. Turning centers, on the other hand, create continuous chips as they remove material through rotational cutting.
6. Precision and Surface Finish
Both machining centers and turning centers can achieve high levels of precision. However, machining centers are known for their higher accuracy in complex geometries, while turning centers excel in achieving excellent surface finish on cylindrical parts.
| Machining Centers | Turning Centers | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Milling, drilling, tapping, and more | Rotational machining |
| Processes Supported | Multi-axis machining | Single-axis machining |
| Tool Features | Various tool holders for different cutting tools | Tool holders for turning operations |
| Uses | Machining complex parts | Creating cylindrical parts |
| Cutting Attributes | Produces chips | Creates continuous chips |
| Precision and Surface Finish | High accuracy, complex geometries | Excellent surface finish on cylindrical parts |
By understanding these top six differences, you can make more informed decisions when choosing between a machining center and a turning center for your CNC machining needs. Whether you require the versatility of a machining center or the specialized capabilities of a turning center, selecting the right machine for your application is crucial for achieving optimal results.
What is CNC Turning?
CNC turning is a fundamental process in the field of rotational machining. It involves the use of a lathe machine to shape cylindrical parts with precision and efficiency. The workpiece, which is the material to be machined, is securely held in place by a chuck while it rotates at high speed. The cutting tool, on the other hand, remains stationary and removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape.
CNC turning is widely utilized in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where the production of cylindrical components is essential. The process is known for its ability to achieve excellent surface finishes and high dimensional accuracy. By carefully controlling the rotation of the workpiece and the movement of the cutting tool, CNC turning enables the creation of complex geometries and intricate details.
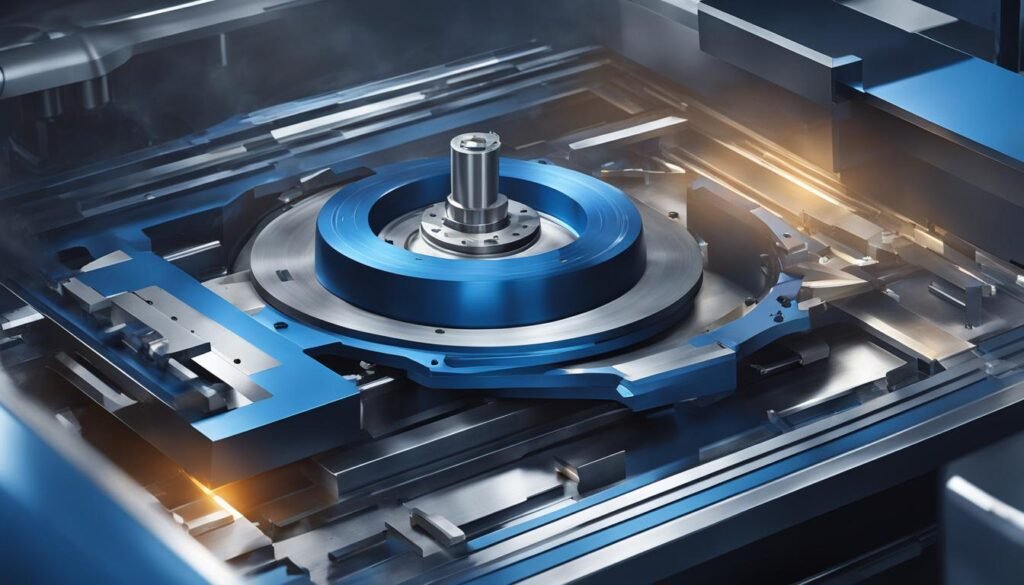

One of the key advantages of CNC turning is its versatility. It can be used to machine a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Whether it’s brass, aluminum, or stainless steel, the lathe machine and its cutting tools can handle the specific requirements of each material. This flexibility makes CNC turning a cost-effective and efficient solution for various manufacturing projects.
Key Elements of CNC Turning:
- Lathe: The primary machine used for CNC turning. It rotates the workpiece and holds it in place during the machining process.
- Rotation: The workpiece rotates at a high speed, allowing the cutting tool to remove material and shape the desired geometry.
- Workpiece: The material being machined, typically in the form of a cylinder or rod.
- Chuck: A device that securely holds the workpiece in place while it rotates.
- Cylindrical Parts: The components produced through CNC turning have a cylindrical shape, making them suitable for various applications.
CNC turning plays a vital role in modern manufacturing processes, providing the precision and efficiency required for the production of high-quality cylindrical parts. By harnessing the capabilities of lathe machines and advanced CNC technologies, manufacturers can achieve exceptional results in terms of surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall part quality.
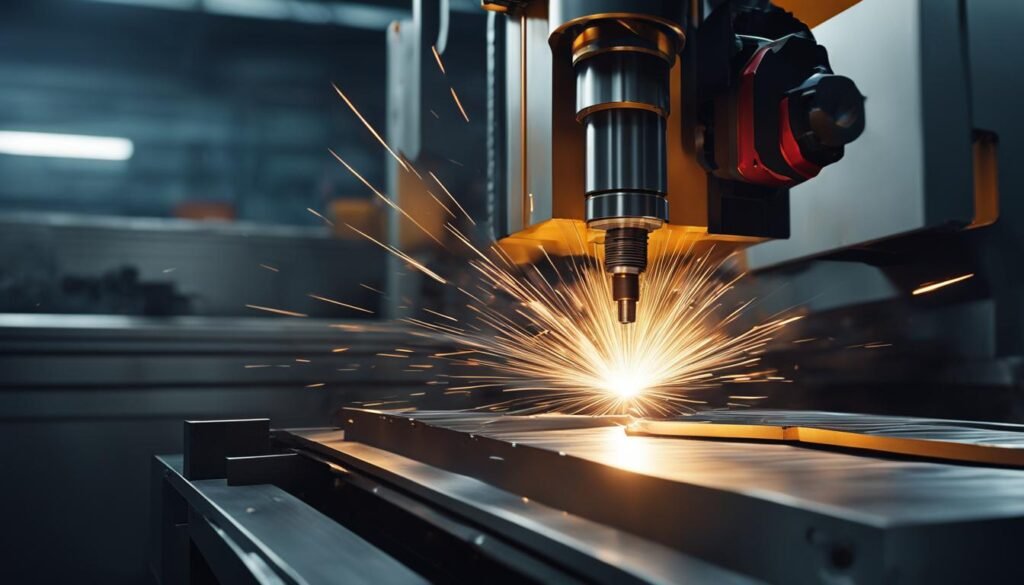
What is CNC Milling?
CNC milling is a cutting-edge machining process that utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) technology, cutting tools, and multiple axes to shape and machine complex parts with precision and efficiency. It is a versatile technique that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering tremendous capabilities for creating intricate geometries and achieving high levels of accuracy.
One of the key features of CNC milling is its ability to perform multi-axis machining. This means that the milling machine can move along multiple axes simultaneously, enabling the creation of complex shapes and contours. The most common types of CNC milling machines are 3-axis and 5-axis machines. A 3-axis milling machine can move along the X, Y, and Z axes, while a 5-axis machine adds rotation around the X and Y axes, allowing for even greater flexibility and precision.
With CNC milling, a variety of cutting tools can be used to remove material from the workpiece. These tools include end mills, face mills, ball mills, and more, each designed for specific purposes and applications. The choice of cutting tool depends on factors such as the material being machined, the desired surface finish, and the complexity of the part.
CNC milling is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, where the production of complex and precise parts is essential. It offers advantages such as improved accuracy, faster production times, reduced labor costs, and the ability to machine a wide range of materials. Whether it’s prototyping, small-batch production, or large-scale manufacturing, CNC milling provides a reliable and efficient solution for machining complex parts.

Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a machining center and a turning center in CNC machining allows you to make informed decisions for your precision engineering needs. By choosing the right method based on the requirements of your project, you can ensure cost-effective and efficient manufacturing processes.
CNC machining offers a wide range of capabilities, and the selection between a machining center and a turning center depends on the specific requirements of your manufacturing project. Whether you need to create complex parts with intricate geometries or produce cylindrical components in high volume, each type of machine has its strengths and applications.
For precision engineering, it is crucial to consider factors such as the desired level of automation, the need for versatile machining processes, and the importance of surface finish and precision. By assessing these factors, you can determine whether a machining center or a turning center is the right choice for your project.
In conclusion, CNC machining provides the tools and technology to bring your manufacturing projects to life. By understanding the differences between machining centers and turning centers, you can optimize your production processes, achieve the desired level of precision, and ultimately, deliver high-quality products efficiently and cost-effectively.
FAQ
What is the difference between a machining center and a turning center?
Machining centers are versatile CNC machines that encompass various processes like milling, drilling, and tapping, while turning centers specialize in rotational machining operations.
What processes are supported by machining centers?
Machining centers support processes such as milling, drilling, and tapping.
What processes are supported by turning centers?
Turning centers excel at rotational machining operations.
What are the tool features of machining centers?
Machining centers offer multiple axes movement and diverse machining processes.
What are the tool features of turning centers?
Turning centers provide single-axis machining.
What are the uses of machining centers?
Machining centers are ideal for creating complex parts and components.
What are the uses of turning centers?
Turning centers are suitable for high-volume production of cylindrical parts.
What are the cutting attributes of machining centers?
Machining centers offer high accuracy and excellent surface finish.
What are the cutting attributes of turning centers?
Turning centers provide excellent surface finish and are suitable for high-volume production.
What kind of chips are produced by machining centers?
Machining centers produce chips with various shapes and sizes.
What kind of chips are produced by turning centers?
Turning centers produce chips that are long, continuous, and helical in shape.
What is CNC turning?
CNC turning is a process that involves rotational machining using a lathe machine to shape cylindrical parts.
What is CNC milling?
CNC milling is a process that involves the use of cutting tools and multiple axes to shape and machine complex parts.
Source Links
- https://www.mastercam.com/news/blog/milling-turning-and-mill-turn-what-are-the-differences/
- https://www.angleroller.com/machining-center/machining-center-and-turning-center-comparison-unraveling-the-differences-and-choosing-the-right-machine-for-your-needs.html?amp=1
- https://eglvaughan.co.uk/difference-between-cnc-turning-and-milling/